- Sales SupportContact Sales
- Call us at: +(86) 15211074652
- Send us a email at: info@zr-fibercable.com
Common questions and precautions for beam tube optical cables
Beam tube optical cables are a type of fiber optic cable that is designed for use in beam tubes. Beam tubes are used in particle accelerators, synchrotrons, and other scientific instruments where precise optical transmission is required. In this article, we will discuss common questions and precautions for beam tube optical cables.
Common Questions for Beam Tube Optical Cables
What is the Attenuation of Beam Tube Optical Cables?
The attenuation of beam tube optical cables refers to the loss of signal strength that occurs as the signal travels along the cable. The attenuation of beam tube optical cables is generally low, with typical values of less than 0.3 dB/km. However, attenuation can be affected by various factors such as cable length, bending radius, and wavelength.
What is the Bandwidth of Beam Tube Optical Cables?
The bandwidth of beam tube optical cables refers to the range of frequencies that the cable can transmit. The bandwidth of beam tube optical cables is generally high, with typical values of 10 GHz or higher. However, bandwidth can be affected by factors such as cable length, connector type, and mode of operation.
What is the Minimum Bending Radius for Beam Tube Optical Cables?
The minimum bending radius for beam tube optical cables refers to the smallest radius that the cable can be bent without affecting its performance. The minimum bending radius for beam tube optical cables is typically specified by the manufacturer and can vary depending on the cable type and diameter. Bending the cable beyond the minimum radius can lead to increased attenuation and signal distortion.
What Connectors are Used with Beam Tube Optical Cables?
Beam tube optical cables typically use standard optical connectors such as FC, SC, and LC. These connectors are designed to provide a secure and reliable connection between the cable and the instrument. The choice of connector depends on the specific application and the requirements of the instrument.
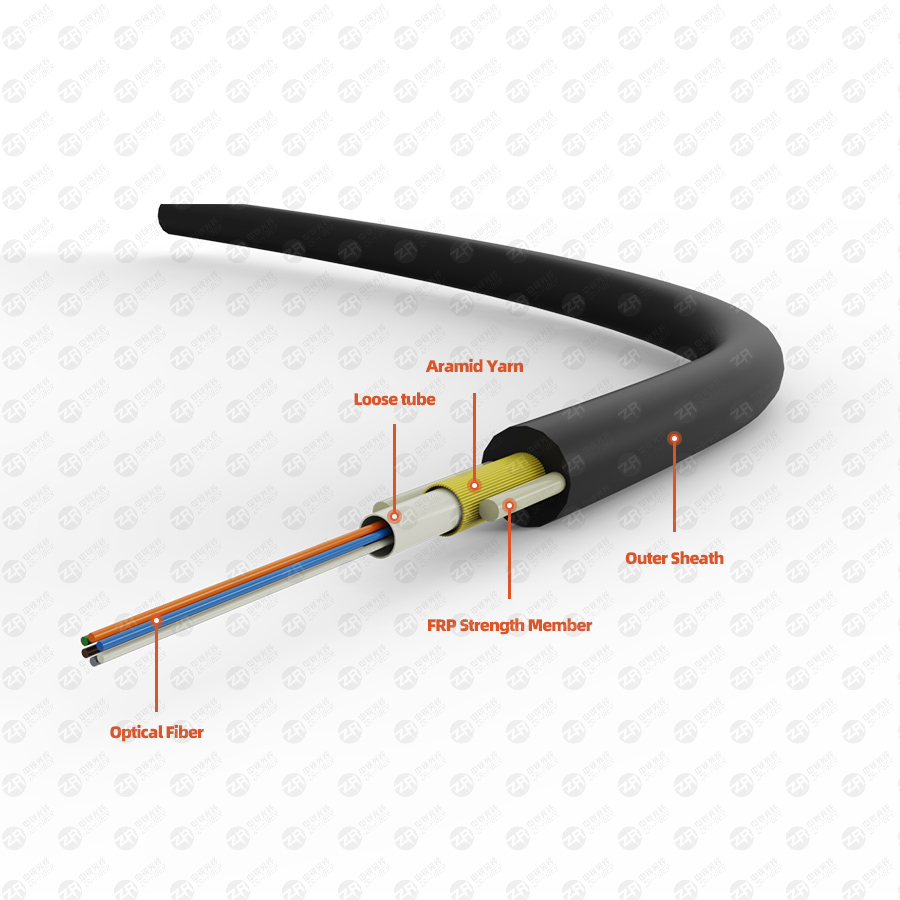
Precautions for Beam Tube Optical Cables
Proper Cable Handling
Beam tube optical cables are delicate and require proper handling to prevent damage. It is important to avoid bending the cable beyond the minimum radius, twisting the cable, or applying excessive force to the connectors. Additionally, the cable should be stored in a clean and dry environment to prevent contamination and damage.
Proper Cable Installation
Proper cable installation is important to ensure reliable performance of beam tube optical cables. The cable should be installed according to the manufacturer's guidelines and the instrument's requirements. Care should be taken to avoid sharp bends, tight turns, and excessive tension on the cable.
Proper Cable Testing
Proper cable testing is important to verify the performance of beam tube optical cables. Testing should be done using specialized equipment to measure parameters such as attenuation, bandwidth, and reflection. Testing should be done before installation, after installation, and periodically during the lifetime of the cable.
Proper Cable Maintenance
Proper cable maintenance is important to ensure the longevity of beam tube optical cables. Regular inspections should be done to check for damage, contamination, or wear. Cleaning should be done using specialized tools and solvents to avoid damage to the cable. Additionally, damaged or worn cables should be replaced promptly to prevent downtime.
Conclusion
Beam tube optical cables are critical components in scientific instruments that require precise optical transmission. Understanding the attenuation, bandwidth, minimum bending radius, and connector types of beam tube optical cables is important to ensure reliable performance. Precautions such as proper cable handling, installation, testing, and maintenance are important to prevent damage and ensure longevity. By following these precautions and understanding the requirements of beam tube optical cables, businesses can ensure reliable and precise optical transmission in their scientific instruments.
You might be interested in
We use cookies to ensure that we give you the best experience on our website. By clicking on "Accept" or continuing to use this site, you agree to our use of cookies in accordance with our Cookie Policy .You can refuse the use of cookies here.
Accept

